2024 State of Accreditation Report
We are pleased to share insights from AACSB accreditation visits over the past academic year, providing AACSB members with a collective learning opportunity. In the spirit of continuous improvement, this report offers key outcomes, best practices, and future opportunities.
Have feedback? We want to hear from you!
2023–24 Accreditation Outcomes
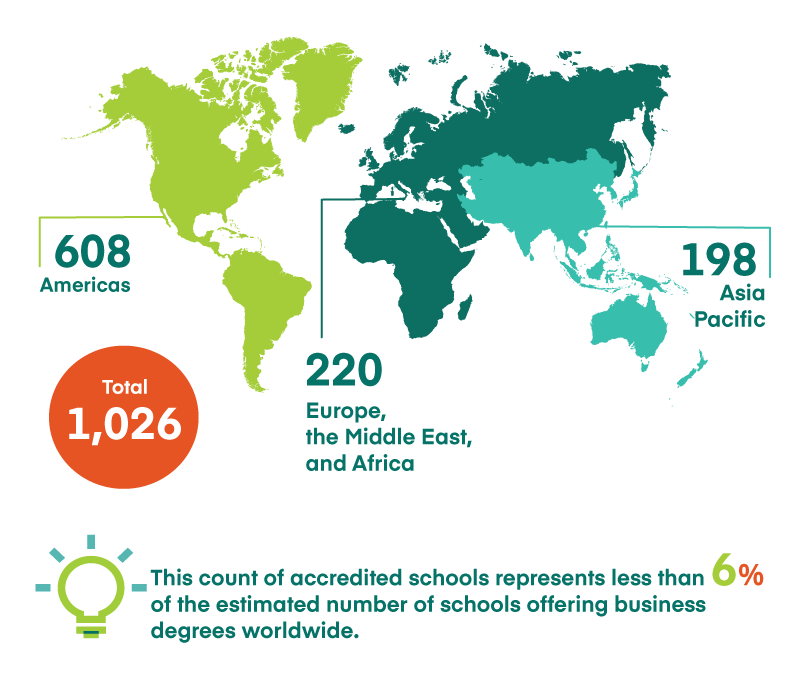
Business Accreditation
Business Accreditation as of June 30, 2024
Accreditation Outcomes, July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024
Notes:
Data displayed are as of June 30, 2024.
Total number of extensions: 188 (includes business and accounting).
Total number of schools achieving business accreditation: 38.
Total number of schools achieving accounting accreditation: 0.
Initial Business Accreditation
Number of Schools in Process as of June 30, 2024
| Total: 278 |
Initial Accreditation Visits, July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, Outcomes by Region
| Total: 43 |
Continuous Improvement Review
Continuous Improvement Review Visits, July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024, Outcomes by Region
| Total: 210 |
2023–24 Accreditation Insights
Business Standards Most Cited by Peer Review Teams
Schools With Visits Between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024, With Accredit and Extend Recommendations
In peer review team reports for both initial accreditation and continuous improvement review (CIR) visits in 2023–24, the following standards were most frequently cited as areas requiring improvement by the school’s next visit.

Standard 9 was mentioned in 94 percent of the decision reports sent, not due to peer review team findings but based on guidance from the accreditation operating committees, which emphasized the need for schools to strengthen their strategic approaches to societal impact.
Source: School decision reports.
Standard 3: Faculty and Professional Staff Resources—Common Issues |
- Faculty Qualifications and Sufficiency: Peer review teams frequently note that schools should more systematically track faculty qualifications and sufficiency ratios to monitor alignment with expected ratios. Feedback in decision reports also indicates that schools must review and refine their qualifications criteria to ensure alignment with their missions and strategic initiatives.
- Faculty Development and Support: Schools are advised to support faculty development by ensuring that faculty members have adequate time and resources to produce high-quality research and meet the school's strategic goals. In cases where administrators are held to different qualification standards than faculty, schools must have formal policies that differentiate criteria for faculty involved in significant administrative duties.
- Staffing Capacity for Strategic Growth: In light of enrollment growth and enhanced international profiles, schools are advised to invest in staffing capacity. This includes increasing the number of both faculty and professional positions to support mission-related activities and the needs of stakeholders.
For more information on insights related to Standard 3, please see Faculty Insights.
Standard 1: Strategic Planning—Common Issues |
- Strategic Plan Alignment and Implementation: Peer review teams have noted that while schools understand the need to align the strategic plan with the school mission, the strategic initiatives often lack specificity. Without specific goals and initiatives, schools face challenges with implementing, executing, and monitoring strategic plans.
- Marketing Plan and Strategy: Peer review teams highlight the importance of having a comprehensive marketing strategy to maximize program enrollment. This approach involves establishing specific enrollment targets and facilitating curriculum enhancement and faculty development.
- Societal Impact Integration: Schools are expected to intentionally incorporate societal impact into their strategic plans by selecting a focus area or areas and linking to goals that align with the school’s mission, demonstrating impact over time.
Standard 5: Assurance of Learning—Common Issues |
- Continuous AoL System Improvement: Schools are advised to continually enhance their assurance of learning (AoL) systems, ensuring that they align with the school’s mission and facilitate curriculum improvements based on assessment of learning outcomes. AoL evidence should clearly illustrate how these systems are used for ongoing improvement.
- Curricular Alignment With Learning Outcomes: Schools should demonstrate alignment between the assessment of learning outcomes and curriculum changes, focusing on program-level improvements rather than course-level adjustments, since AoL is focused on demonstration of learning outcomes at the degree program level.
- AoL Impact: Schools are advised to provide more robust evidence of how they are “closing the loop” in their AoL processes by actively using assessment data to inform and drive improvements. This involves refining the execution of AoL plans and clearly demonstrating the specific improvements that have been implemented based on assessment outcomes.
Standard 5 was cited for 78 percent of schools with a CIR2 recommendation.
Faculty Insights
Faculty Qualification Ratios for Schools With Visits in 2023–24

Note: The category of Additional Faculty, representing 4 percent, is not included above. Values have been rounded and may not equal 100 percent.
The overall participating faculty ratio for schools visited in 2023–24 is 85 percent.
Scholarly Academic Ratios by Discipline
Most Frequently Reported Disciplines
Intellectual Contributions Produced
Count of Intellectual Contributions Produced Over 5 Years by Schools Visited in 2023–24
Note: Values have been rounded and may not equal 100 percent.
Portfolio of Intellectual Contributions
Supplemental Accounting Accreditation
Initial Accreditation and Continuous Improvement Review Accounting Visit Outcomes, July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024
| Total: 43 |
Accounting Standards Most Cited by Peer Review Teams for Visits Between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024, With Extend Recommendations

Source: Accounting Unit Decision Reports
Standard A1: Accounting Academic Unit Mission, Impact, and Innovation |
- Resource Allocation: Accounting programs should ensure that their strategic plans are well-aligned with their mission and vision and clearly focused on resource allocation. The plans should also include marketing and recruitment strategies to support program growth. Accounting programs should also establish responsible parties for goals and monitor progress.
Standard A4: Accounting Curriculum Content and Assurance of Learning |
- Technology Integration in Curriculum: Accounting programs should more intentionally integrate current and emerging technologies such as generative AI into their curriculum. Peer review teams noted the importance of key stakeholder involvement to ensure appropriate technologies are employed in the curriculum.
- AoL Process Enhancement: Accounting programs should develop both direct and indirect measures to ensure that learners achieve the desired competencies. These measures may include professional exam results and alumni or employer satisfaction surveys.
- Curriculum Innovation and Alignment With Industry Standards: Accounting programs should continually innovate their curricula to align with the evolving needs of the accounting profession, including updates driven by changes in CPA exam content. Programs should also ensure that curriculum adjustments also reflect assessment outcomes, not just external industry changes.
Standard A6: Accounting Faculty Sufficiency, Credentials, Qualifications, and Deployment |
- Succession Planning for Faculty Turnover: Accounting programs should develop succession plans to address potential faculty turnover, particularly in leadership roles. Plans should include strategies for maintaining sufficient levels of Scholarly Academic faculty during periods of significant turnover.
- Faculty Deployment Strategy: Accounting programs should review their faculty deployment strategies to better align with AACSB standards while ensuring that qualified faculty are deployed across all degree programs to support high-quality learner success and achievement of learning competencies.
Volunteers
Anthony Nelson
Dean, School of Business
North Carolina Central University
Volunteer Representation for 2023–24
Notes:
This list includes individuals who served as a volunteer between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024, in one of the following roles:
• Operating Committee Member (Accounting Accreditation Committee—AAC; Accounting Accreditation Policy Committee—AAPC; Business Accreditation Policy Committee—BAPC; Continuous Improvement Review Committee—CIRC; Initial Accreditation Committee—IAC)
• Mentor (business or accounting)
• Team Chair (business or accounting)
• Team Member (business or accounting)
Only individuals who agreed to be listed are included. If your name does not appear and you served on one of the roles listed above between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024, and would like to be added, please contact us at [email protected]. Thank you.
Satisfaction With Accreditation Experience
| 94% | school satisfaction with 2020 standards visit |
| 99% | increased value of 2020 standards |
| 97% | school satisfaction with myAccreditation |
| 97% | volunteer training preparation for accreditation visit |
| 97% | satisfaction with volunteer training |
| 886 | volunteers have been trained overall on the 2020 standards |
| 132 | volunteers were trained in 2023–24 |
| 170 | volunteers completed the refresher training |
Best Practices and Innovations
















Societal Impact
Schools continue to leverage the accreditation standards to identify key focus areas and develop societal impact plans, ensuring that their goals and outcomes contribute to addressing some of society’s most significant challenges. The Stockholm Resilience Centre’s SDG Wedding Cake Model was employed to classify the initiatives reported by schools in 2023–2024. The model organizes these initiatives into three categories: Economy, Biosphere, and Society.
![]()
Societal Impact Focus Areas
Initiatives Reported From CIR Visits, Between July 1, 2023, and June 30, 2024
Societal Impact Exemplars
![]()
Nanjing University: The Nanjing University (NJU) Business School has a significant influence in serving society through initiatives such as the Jiangsu Development Summit, Yangtze Industrial Economic Research Institute, and Management Research Academic Community Construction. The Jiangsu Development Summit, organized by NJU Yangtze River Delta Economic and Social Development Research Center since 1997, is held once a year and the highest leaders of Jiangsu Province have attended each summit. The summit has now become the most important policy consultation platform for Jiangsu Province. It is also a platform to promote scientific and democratic decision-making for the provincial government and has made significant contributions to the economic development of Jiangsu Province.
![]()
Fordham University: Fordham University’s Gabelli School of Business exemplifies societal best practices through its innovative Ground Floor course, which integrates environmental, social, and governance principles and stakeholder capitalism, teaching students to use business skills for positive societal impact. The school’s Responsible Business Center furthers these efforts by advancing sustainability solutions and fostering interdisciplinary engagement, preparing future leaders to build sustainable communities and strong institutions. Additionally, the Gabelli Center for Global Security Analysis and O’Shea Center for Credit Analysis and Investment specialize in investment and credit analysis, equipping students with the knowledge to make responsible financial decisions that support ethical business practices.
![]()
Technische Universität München: The Technische Universität München (TUM) School of Management has infused sustainability into curricula, preparing students to tackle pressing global challenges such as the climate crisis and energy shortages. Specifically, the Master of Science in sustainable management and technology equips students with the business knowledge and methodologies to develop sustainable technologies, products, and processes. Graduates gain interdisciplinary skills to shape the transition toward sustainable companies and can work as analysts, innovators, or mediators. Additionally, the school offers a new specialization for the Master in Management & Technology program that focuses on renewable energies including solar, wind, biogas, and hydrogen. This program involves collaboration with the TUM SEED Center, promoting student exchanges with partners in the Global South to address energy challenges.
Looking Forward
As we reflect on the continuous evolution of the accreditation process, it’s essential to look ahead to the 2024–25 peer review visits. The following four topics highlight key areas that will require attention and provide guidance for both peer review teams and accredited and in-process schools.
Transition to the 6-Year Continuous Improvement Review Cycle
The shift to a six-year CIR cycle marks a significant change in our accreditation process, and it has understandably generated many questions from our member schools. The most frequently asked questions involve the timing and frequency of reports, how to maintain momentum in continuous improvement efforts, and the implications for schools that are mid-cycle.
This change is designed to provide schools with more flexibility and time to implement and demonstrate meaningful improvements. We encourage schools to focus on long-term strategic goals and to use the additional time to enhance their processes and outcomes.
Visit the AACSB website to access additional details on the transition to a six-year cycle. Peer review teams will play a critical role in ensuring that schools remain focused on continuous improvement throughout the extended cycle, providing constructive feedback and guidance. All schools should have received communication from AACSB and should be aware of when their next visit is. If you are unsure, please reach out to us at [email protected].
Addressing the Challenge of Predatory Journals
The proliferation of predatory journals presents a significant challenge to the integrity of academic research. It is imperative that schools take proactive steps to ensure that their faculty are not inadvertently publishing in these journals, which can undermine the credibility of their research output.
Peer review teams should carefully examine the quality of journals in which faculty publish and encourage schools to implement robust vetting processes. Schools should educate their faculty on how to identify predatory journals, use recognized journal rankings and databases, and encourage collaboration with reputable publishers. This effort is crucial in maintaining the high standards of academic rigor that AACSB accreditation represents.
Clarifications on Indirect Measures Within Assurance of Learning
A recurring area of confusion within AoL is the role of indirect measures. There are two distinct types of indirect measures: those that close the loop on specific learning competencies and those that provide general insights into the overall success of graduates but are not tied to specific learning outcomes.
The former, such as employer surveys that directly assess a specified learning competency for a specific degree program, are appropriate for AoL and can be used to make data-driven improvements to curriculum and instruction. The latter, such as general employment data, while valuable, do not meet the requirements for AoL as they do not provide actionable insights on student learning. Peer review teams should ensure that schools understand this distinction and are using appropriate indirect measures to inform their AoL processes.
Introducing AACSB Accreditation Chatbot
Earlier this year, we launched our AACSB website chatbot, an innovative tool available on all pages of our website. This publicly accessible chatbot draws from a private small language model (SLM) that includes our accreditation standards, interpretive guidance, white papers, website articles, and frequently asked questions. It is designed to help users navigate the complexities of AACSB accreditation and answer other general questions they may have related to events, membership, and more. This tool is particularly valuable for schools seeking quick, reliable answers to accreditation-related questions.
In addition, a more comprehensive version of this chatbot will be available within myAccreditation later this year offering even deeper insights by drawing from a broader SLM that includes our accreditation policies and procedures, along with the documents in the publicly available model.
This technology represents a significant step forward in our commitment to providing accessible, high-quality support to our member schools and peer review teams. As with all AI tools, we remind our members that AI combined with human judgment provides the best result. Our accreditation managers are still available to support schools as they navigate their accreditation journeys.
As we look forward to the 2024–25 academic year, we are confident that these developments will further strengthen the AACSB accreditation process, ensuring that it continues to be a hallmark of excellence in business education. We encourage all schools and peer review teams to engage deeply with these topics and to reach out with any questions or feedback. Together, we will continue to advance the quality and impact of business schools globally.
Explore prior year reports:




